Shopping has never been easier. It's one click away whether you're using a mobile phone, PC, or tablet.You can browse any style, category, and item anytime, anywhere. But online shopping isn't only about clothes and accessories. Today, it's just as common to order a burger while chilling on your sofa as physically going to fast food to buy it.
Online retail has made possible what our ancestors wouldn’t consider in their wildest imagination. Not only can you purchase nearly anything scrolling virtual stores, but you can also start your business and sell products and services.
Ecommerce is a simple term encompassing selling and buying goods online using different devices. However, as a continuously evolving trade, eCommerce has expanded into specific subsets, including mobile eCommerce.
But you may not know there’s a difference between eCommerce and mobile eCommerce. This article will guide you through the meaning and main differences between the two.
What is eCommerce?
Electronic commerce or eCommerce refers to online sales and purchases of services and goods. It dates back to 1994 when American entrepreneur Dan Kohn created the website NetMarket and used it to sell the CD Ten Summoner’s Tales by Sting to a friend in Philadelphia.
Although it may come as a surprise that eCommerce is not a novel way for retailers to sell things, its growth only accelerated during the pandemic. The lockdown measures forced businesses to focus on online transactions, and that trend will continue throughout 2024. However, eCommerce isn’t only about physical products. It also involves subscriptions (e.g., paying for monthly streaming) and digital goods, such as e-books or music.
What is Mobile eCommerce?
Although there’s no strict mobile eCommerce definition, mCommerce stands for buying and selling products and services through mobile devices such as tablets and smartphones. This digital commerce extension has become increasingly significant with the widespread use of mobile technology.
It includes various transactional activities, ranging from online shopping to in-app purchases. Since mCommerce has made on-the-go shopping more convenient due to being able to access online stores and services anytime, its popularity is reaching incredible heights.
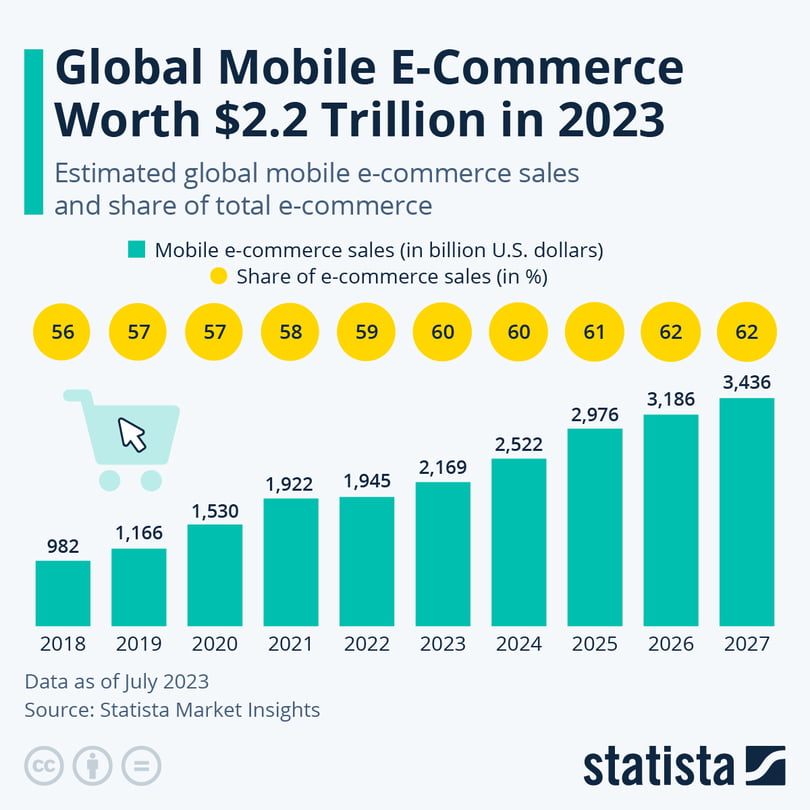
Statista found that mCommerce has hit $2.2 trillion in 2023 and now encompasses 60 percent of all e-commerce sales globally. Its share has been consistently growing since 2018 and will likely climb to 62 percent in 2027.
As mCommerce becomes more sophisticated, eCommerce owners must ensure to keep up with security standards. That requires advanced secure payment gateways and authentication measures to safeguard sensitive information. Moreover, they must integrate mobile wallets and contactless payments to streamline the checkout process.
But what precisely makes mCommerce different from eCommerce?
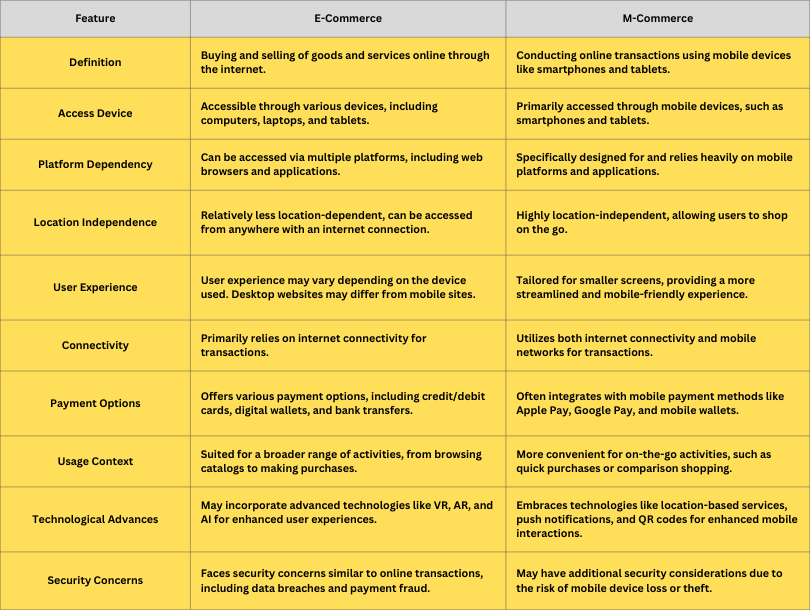
What is the Difference Between Mobile eCommerce and eCommerce?
Even though mobile eCommerce and eCommerce are related concepts, one doesn’t necessarily require the other for existence. For instance, retailers can have eCommerce without establishing mCommerce.
But that’s easier to understand when knowing what characteristics make these two different.
The following are the top differences between mCommerce and eCommerce.
Transportability
In general, eCommerce uses laptops and PCs to facilitate trade and online transactions, meaning it relies on stationary technology. You can still move them around, but these devices are less mobile than phones.
That’s among the reasons many prefer mCommerce. Consumers often have no patience to open a laptop and look for new jeans or shoes.
People love portability and convenience, which is why retailers should invest in a high-quality mCommerce site. An easily accessible website or app can dramatically increase sales and expand the customer base.
Push Alerts
Mobile devices allow push notifications, making mCommerce more attractive. These don’t interfere with what a customer is doing as much as being a part of a mailing list and receiving mass promotional emails, which typically lack personalization.
Retailers also think that push alerts are less overwhelming and more efficient. Unlike promo emails, these won’t land in the spam box, and customers are less likely to ignore them.
Instead, people receive them instantly, one of the reasons 52 percent perceive them as helpful. In general, these alerts can increase eCommerce CRO.
They also have higher odds of being seen because they can include high-quality product photos. Customers can easily open and check them out with a single tap on the screen.
Location Tracking
Both mCommerce and eCommerce can use GPS and Wi-Fi tracking features and data to customize product and advertising suggestions. But the difference is that mCommerce asks for location tracking permission.
That gives customers more control over their data privacy. Yet, if they allow mCommerce GPS tracking, they will enjoy a better experience thanks to tailored recommendations.
For instance, mCommerce can use geofencing, which triggers location-specific notifications or promotions. On the flip side, eCommerce retailers don’t have enough data to develop more refined customer profiles due to only seeing their home location.
Marketing and Ads
Making a customer feel like retailers crafted advertising specifically for them is among the most powerful marketing techniques. That encourages them to place an item in the cart and finalize their purchase, often converting one-time shoppers into repeat customers.
Unlike mCommerce, eCommerce has more limited capabilities in this regard. Although these retailers can use push notifications, mCommerce allows for more instantaneous advertising and notifying people about exclusive sales and their favorite products being back in stock.
Omnichannel
Unlike eCommerce, mCommerce centers its omnichannel strategy around mobile devices, prioritizing seamless experiences on smartphones and tablets, often leveraging location-based services. It tailors the user journey specifically for mobile interfaces and engages customers in real time based on their mobile device context.
In contrast, eCommerce takes a broader omnichannel approach, integrating various channels such as desktop websites, mobile apps, and physical stores. The emphasis is on consistency across diverse platforms, ensuring a unified experience as customers transition between devices and channels.
While both embrace omnichannel principles, mCommerce has a mobile-centric focus compared to eCommerce’s comprehensive integration across various channels.
Security
Online transactions require an advanced security level, and eCommerce and mCommerce handle this matter differently. The former focuses its security measures on traditional online platforms, employing standard encryption protocols and secure payment gateways.
Moreover, eCommerce adapts its methods to desktop environments and may rely on technologies like SSL and TLS for secure transactions. Meanwhile, mCommerce security extends to mobile devices, emphasizing protecting transactions on mobile apps and mobile-optimized websites.
When clarifying the difference between eCommerce and mobile commerce, it’s essential to mention that mCommerce typically has secure mobile wallets and two-factor authentication. It also addresses specific vulnerabilities associated with portable devices.
Transaction Speed
Slightly longer transaction times are more common in eCommerce because mCommerce leverages mobile devices’ immediacy, allowing for quicker and more efficient transactions. That results in different engagement levels, with m-commerce capitalizing on the on-the-go nature of mobile devices for faster and more immediate transaction experiences compared to the often slightly lengthier process associated with desktop-based e-commerce.
The Key Benefits of Mobile eCommerce
The following benefits of mobile eCommerce are essential for businesses.
More Accurate Customer Data
Businesses can accomplish more personalized customer communication using mCommerce. They can leverage beacon analytics and technology, small, wireless devices that transmit signals to nearby smart devices, such as smartphones or tablets.
For instance, when a consumer with a mobile app on their device enters the store, the beacon detects the presence of their device. The beacon communicates with the mobile app, providing information or triggering actions based on the consumer’s location in the store. Retailers can use that data to customize communication, creating personalized messages, promotions, or product recommendations based on the individual’s preferences, purchase history, or real-time behavior.
Improved Customer Experience
One of the most significant benefits of mCommerce is that it helps create a more tailored customer experience by providing instant, location-aware interactions. Retailers leverage features like push notifications, personalized offers, and real-time updates, customizing engagement to a customer’s immediate context.
This dynamic interaction bridges the online and offline shopping experience, fostering customer loyalty through smooth, convenient, and personalized transactions that exceed the capabilities of traditional eCommerce platforms.
Reduced Costs and Higher Revenues
The instantaneous accessibility of mobile platforms facilitates agile marketing strategies, promoting cost-effective, targeted campaigns. Moreover, in-app purchases, location-based promotions, and seamless checkouts enhance user engagement, translating to increased sales and revenue.
The ease of mobile transactions also minimizes cart abandonment rates. As a result, mCommerce’s flexibility, lower operational overhead, and enhanced revenue streams position it as a cost-efficient and revenue-boosting solution compared to traditional eCommerce models.
The Impact of Mobile E-commerce on B2B
Businesses are witnessing a paradigm shift as mobile devices become indispensable tools for streamlined transaction processes, order management, and relationship-building. Active mCommerce integration in B2B environments leads to faster decision-making, eliminating geographical constraints, and fostering real-time collaboration.
But mCommerce’s impact extends beyond transactional convenience; it cultivates a dynamic ecosystem where personalized experiences and data-driven insights are paramount. B2B professionals have more control over on-the-go access to catalogs, pricing information, and customer histories, revolutionizing client interactions.
Moreover, the agility of mobile platforms enhances responsiveness, enabling businesses to adapt swiftly to market changes. In this era of mobile-driven commerce, understanding the difference between eCommerce and mobile commerce is essential for B2B entities leveraging transformative technologies to gain operational efficiency and a competitive edge.
However, these benefits only come after developing a functional and well-performing mCommerce. Whether you need advice on how to start or the assistance of a creative team, consider partnering up with professionals who can help you with Ecommerce development services.
Are you interested in other similar topics? Check out these helpful resources!