Dead links or broken links, are hyperlinks that don’t work anymore. When clicking on one of these, the intended linked page will fail to load. As you probably know, hyperlinks appear as underlined or highlighted text or images. They take you to other pages within the site you’re currently on or another for various purposes, such as urging you to make a purchase or simply to back up a claim by sharing its source.
Still, why do these links break on your site? Better yet, how do you find broken links and fix them? In this article, we have your answers.
Why Do Links Break?
Before learning how to detect broken links, you should know why they become dead in the first place. Here are the most common reasons:
The Target Page has been Moved or Deleted
The most common culprit behind broken links is a deleted target page or somebody who moved them to a new URL without updating the link in the text. Most often, these deleted or moved pages will show the infamous 404 Not Found error page.
Here’s an example. Let’s say, Amazon creates a temporary sales page and links it across its website. After the sales, the webmasters delete the page but don’t remove the links. In this case, if a customer clicks on these old links, they will get the 404 error, which usually leads to confusion and frustration.
Incorrect URL Formats
Faulty URL formats can lead to 400 bad request errors, which are similar to 404 errors, but happen when there’s something off with the URL you requested.
URL problems can arise whenever you accidentally misspell a link when you add it to your page. It can also happen when someone mistype the URL to the page you’re linking to. This simple error happens because servers cannot make sense of the requests. After all, the format of the URL is invalid, so it returns the 404 error as it rejects the request.
URL or Website Structure Changes
If a site’s structure or URLs change, hardcoded links with the full URL can easily break. For instance, if a page has moved from www.thisexample.com/services to www.thisexample.com/ourstore/services, it can end up in a 404 error if hardcoded links are still pointing users to /services rather than the /ourstore/services URL.
These hard-coded links will keep pointing your visitors to dead ends because the URLs weren’t changed when the site got a new architecture.
Broken Images
There are cases when links redirecting to images become broken. This happens when somebody deletes or moves the image files without making the necessary link updates in the HTML code.
Such errors will display the “missing image” icon as the page still has the image link, but it points to a previous or non-existent file location with the image gone.
Changes to Domain Names
Outbound links can also become broken if they link to migrated external, retired, or redesigned sites. External sites will probably return a Bad Gateway 502 error, indicating that the server cannot be found. This may happen because of domain shifts, rebrands, or site retirements. If the links aren’t updated to showcase the changes, they will keep on directing users to broken URLs.
Bad Plugins
Third-party plugin code links can also break when the platform they use changes their code. For instance, social sharing buttons on your site might no longer work if the social platform, Instagram, Facebook, you name it, changes their code for their share button.
Clicking on these share buttons can easily return 404 errors instead of enabling you to share the content. This happens because your platform is still running the old sharing button code, but the social platform’s servers now only read the updated code for the plugin to work.
How Broken Links Impact Your Site?
So you’ve performed a site audit and noticed that there are a few links that return error messages. What now? Should you wait with them, leave them as they are, or aim to repair them pronto? All in all, it’s better to address these problems as soon as possible.
SEO Repercussions
SEO efforts can be hindered by broken links because of the following:
- Impaired site quality: Google aims to recommend users up-to-date and useful sites. Having several broken links may indicate that your site is maintained poorly or not up to date.
- Wasted link authority: Internal links pass authority between your site and connected pages. This is called link equity. However, when the linked page becomes broken, the authority does not get passed on, rather it wastes away.
- Crawl errors: Google’s bots crawl the internet as they follow links between pages. When one of these bots gets to a broken link, the result is a crawl error, meaning that your site or page cannot fully be crawled nor indexed by Google.
That said, fixing broken links should be a cornerstone of your SEO strategy.
UX Impacts
User experience (UX) can suffer a massive blow from broken links on your site. Users may abandon it if they hit more than one dead end by clicking on them. Let’s say, you are shopping on Amazon but you constantly end up with 404 errors because of broken links.
Chances are, you won’t stay on the site for long. In the case of your visitors, they may perceive your platform as poorly maintained and even untrustworthy.
How to Detect Broken Links
While for smaller sites going over your links can be a simple and quick process, if you are running a massive site (like an eCommerce store) addressing link health can take quite some time. As such, here are a few handy tools that can help you detect broken links.
Site Audit Tools
Different site audit tools crawl your site and signal potential broken links and other crawl errors. Most of these solutions will not only detect potential errors but will also give you recommendations on how you should go about fixing them.
That said, it’s not a bad idea to run these audits regularly so you can stay on top of any link-related issues or other problems that might negatively affect your SEO.
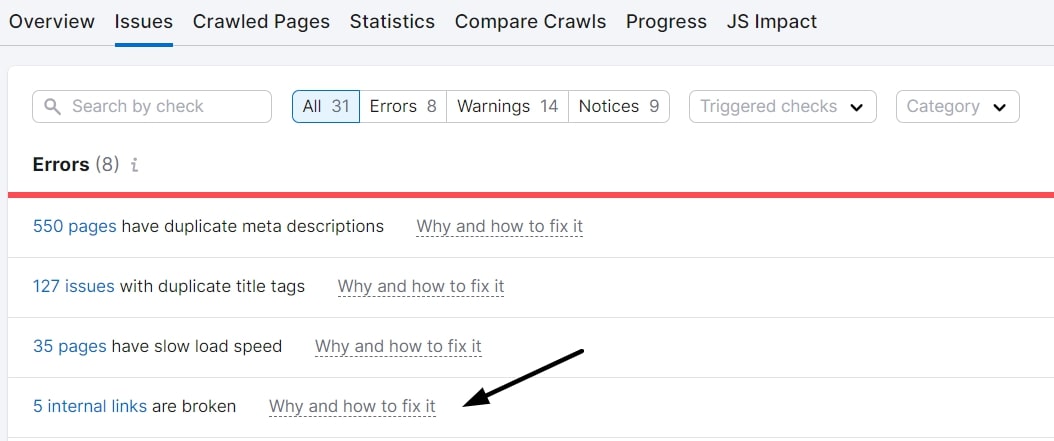
Manual Checks
As we talked about this before, you can also opt to review your site and pages manually to check for broken images or links. This can be tedious but will put you in your site visitor’s shoes.
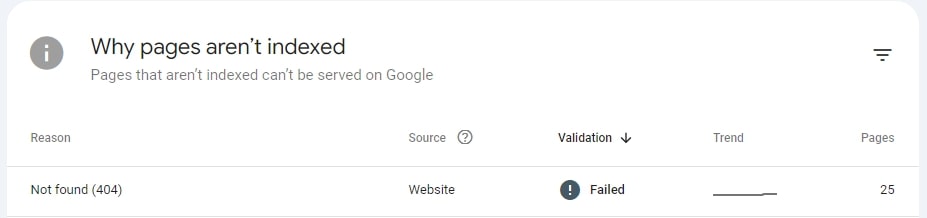
Google Search Console
GSC or Google Search Console is Google’s free tool enabling site owners to monitor the presence of their site in the SERPs. The Page indexing features in the console may also be able to help you find broken links, as the report will display indexed pages that run 404 or other types of errors.
Extensions for Your Browser
Browser tools like Broken Link Checker and other handy solutions can check your pages as you browse and mark any dead ends, i.e., broken links. You can simply install them as Chrome extensions, with a small plugin icon appearing beside the address bar. As you browse your site pages, the extension will scan your links in the background and will report any link-related irregularities on your page.
How to Fix Broken Links
All that’s left to discuss is how you should go about fixing the broken links you’ve come across. Below are four methods that you can use.
Prioritize Your Links
The thing is, you may not need to fix every broken link you come across right away. For lower-priority pages, consider using a custom 404 error page that communicates that the page is no longer active, helping users navigate away with less frustration.
According to Google, custom 404 error message pages are generally considered “medium quality,” especially because they communicate the issue and help the user get to other pages.
Still, that doesn’t mean that you shouldn’t fix all of your broken links. However, if there are a lot of them, it’s always a better idea to fix those that are on your pages with the highest traffic, as these dead ends will hinder your site’s overall experience the most.
You can check in Google Search Console to see just how relevant this error is. As mentioned before, 404 errors prevent the search engine from indexing and crawling your page properly, so if you see an error on some of your most relevant pages, fixing those should be high on your list.
Removing Dead Links
You may consider removing internal links that point to pages that no longer exist. Use your SEO audit tool to check the health of your links, and then, simply just go to the problematic pages and manually remove every broken link that’s no longer relevant.
Redirect Broken Pages
You can also use 301 redirects to forward your visitors from broken pages to other, new, relevant pages. These redirects tell Google and other search engines that the content on the page has permanently relocated and the link should pass authority to the new page’s URL.
Using 301 redirects can greatly improve user experience, even compared to using custom 404 error pages when they accidentally land on broken links.
You can create 301 redirects either by rewriting server rules, given that you have access to hosting, or using built-in redirect manager solutions, or plugins for your content management system.
Update Your URLs
If the linked page still exists but with a brand-new URL, you can update your internal links with the new URL and fix the link breaks.
There are several ways you can go about this:
- You can find dedicated search-and-replace solutions that will update all instances of the old URL with the new one. Several content management systems, such as WordPress, come out of the box with these replacement functions.
- You can also manually edit your old link texts or images for your pages to point to the updated URLs.
- When you link to pages in navigation menus, simply update the target URL in your menu editor if the page’s URL is new/changed/updated.
Get on Top of Your Links
Keeping the links healthy across your site is an important factor in ensuring that everything’s optimized for Google and your visitors. Still, manually checking every page for broken links can be a tedious endeavor during which is easy to forget and make oversights.
As such, you can always opt for digital solutions that can help you with these processes, or better yet, you can partner up with a digital marketing agency (if you haven’t already). The SEO services these agencies provide offer the best understanding of these processes and will ensure you’re always on top of your site’s link health, updating everything in cases of migration, new URLs, deleted pages, and more.





